Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
Overview
If you are using GitLab CI/CD, you can analyze your source code for known
vulnerabilities using Static Application Security Testing (SAST), either by
including the CI job in your existing .gitlab-ci.yml file or
by implicitly using Auto SAST
that is provided by Auto DevOps.
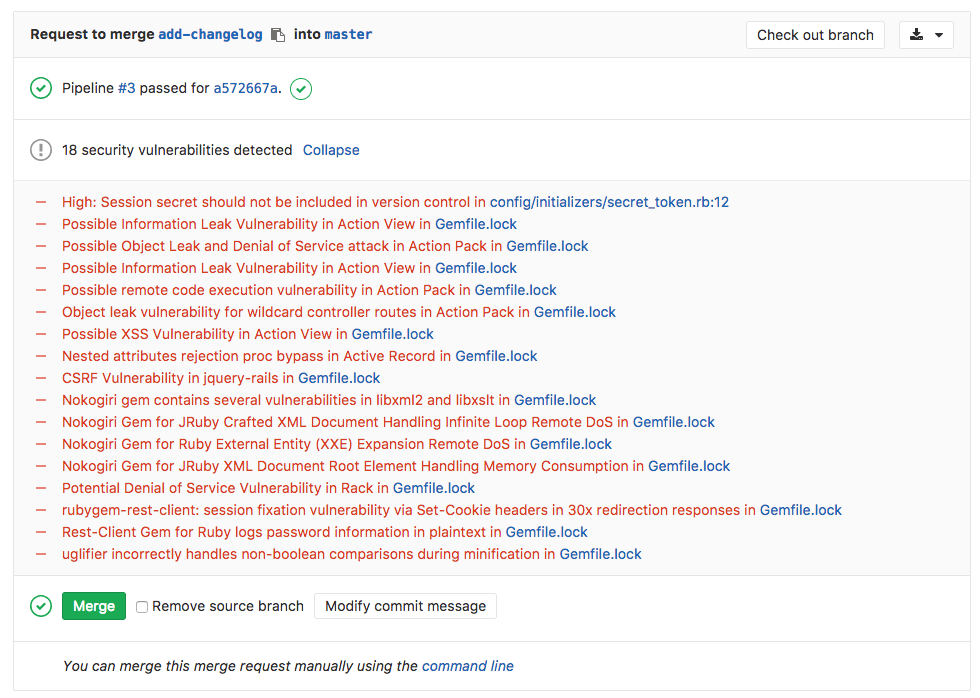
Going a step further, GitLab can show the vulnerability list right in the merge request widget area:
Use cases
- Your application is using an external (open source) library, locked to a
specific version (e.g., via
Gemfile.lock) and the version is known to be vulnerable. - Your code has a potentially dangerous attribute in a class, or unsafe code that can lead to unintended code execution.
How it works
In order for the report to show in the merge request, you need to specify a
sast job (exact name) that will analyze the code and upload the resulting
gl-sast-report.json file as an artifact. GitLab will then check this file and
show the information inside the merge request.
This JSON file needs to be the only artifact file for the job. If you try to also include other files, it will break the vulnerability display in the merge request.
For more information on how the sast job should look like, check the
example on analyzing a project's code for vulnerabilities.